Would you like to transfer an existing project from another platform such as GitHub, or transfer a project from the openCode GitLab instance to another platform (e.g., GitHub, Gitea)? This is referred to as mirroring. There are three methods for doing this:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Push | Mirroring a project from the openCode GitLab instance to another location |
| Pull | Mirroring a project from another location to the openCode GitLab instance |
| Bidirektional | Mirroring in two directions |
Information
In the version of GitLab used by openCode, pull mirroring and bidirectional mirroring are currently not directly possible. Implementation via CI/CD pipelines is possible, but requires advanced knowledge. Instructions for pull mirroring via a CI component can be found below.
How push mirroring works¶
Mirroring involves transferring a project from the openCode GitLab instance to another platform (e.g., GitHub, Gitea). This requires maintainer rights for the project on openCode. The target project (e.g., on GitHub) should already exist. With push mirroring, the source (openCode GitLab instance) actively sends changes to the target (GitHub, Gitea, etc.).
1. Copy the target URL¶
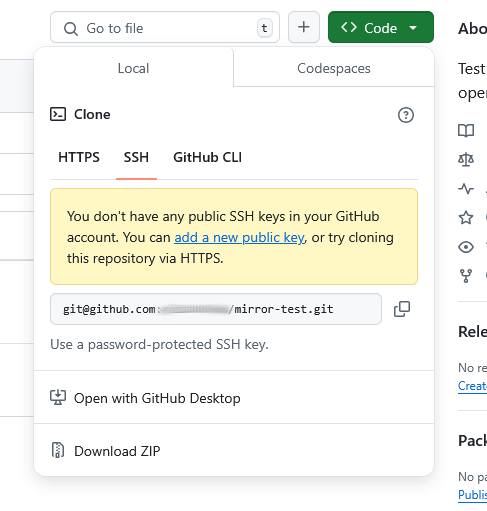
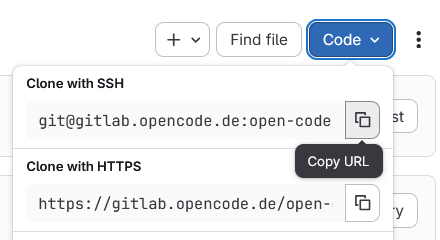
Open the target project (e.g., on GitHub or GitLab) and click on the “Code” button (in GitLab it is blue, in GitHub it is green). In GitHub, select the SSH tab and copy the URL displayed there. In GitLab, select “Clone with SSH” to copy the URL.
Copy URL from GitHub:
Copy URL from GitLab:
 ¶
¶
2. Set up mirroring¶
In your openCode project, go to Settings > Repository. Scroll down to “Mirroring repositories” and click “Add.” Paste the URL you just copied and adjust it as follows:
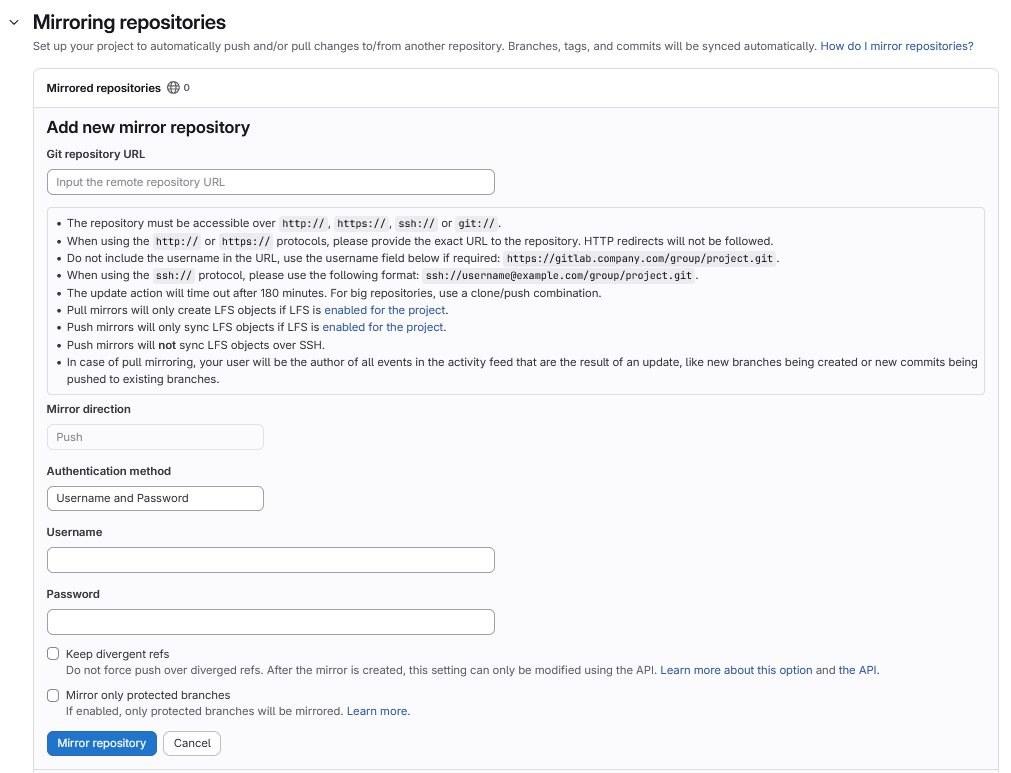
- Add ssh:// before the URL and replace the colon (:) before the project name with a slash (/).
- Select “Public SSH Key” as the authentication method.
- Set the username to “git.”
- Click “Mirror Repository.”
3. Add SSH key¶
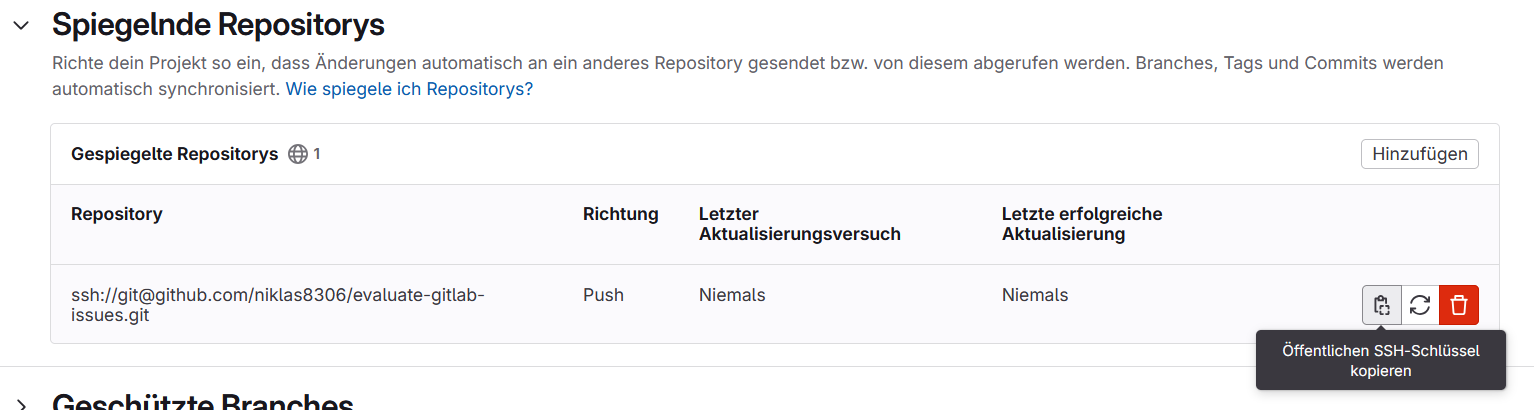
Copy the public SSH key displayed and paste it into the target project as the “Deploy Key.”
To do this, open the page of your empty GitLab project on GitLab and navigate to Settings > Repository. Open the Deployment Keys tab and click on the “Add New Key” button. Now paste the key from the clipboard and choose a meaningful title for your key.
On GitHub, open the page for your empty GitHub project. Click the Settings button in the top right corner and navigate to Security > Deploy Keys in the left sidebar. Confirm Add deploy key, paste the key from the clipboard, and assign a meaningful name here as well.
Note
Mirroring can be done automatically (time-controlled) or manually. Make sure that no private data is transferred unintentionally.
How pull mirroring works¶
The openCode GitLab does not currently allow automatic pull mirroring (mirroring a project from another location to the openCode GitLab instance) via the interface. With pull mirroring, the target initiates synchronization. It regularly queries the source for changes.
However, there is an alternative: implementation via CI/CD pipelines is possible, but requires advanced knowledge. The target (the openCode GitLab instance) starts a pipeline. This pipeline loads the data from the source (e.g., GitHub, Gitea, etc.) into a temporary environment. From there, it is pushed back to the target repository.
In this guide, the projects to be synchronized are referred to as follows:
- Source project: The Git project from which the updates are to be pulled, e.g., on GitHub
- Target project: The Git project on openCode to which the updates are to be applied. The CI/CD configuration is also set here via the
.gitlab-c.ymlfile.
1. Create target project¶
Create an empty target project on the openCode GitLab instance. Create a new branch in this project. If the project has already been imported (e.g., from GitHub), use this repository with a new branch.
Now create the following GitLab CI script (.gitlab-ci.yml) on the newly created branch. Adjust the link of the target project under #Clone only main from GitHubwith the URL of the source project:
You can adjust the target project to be cloned using the TARGET_REPO variable.
Hinweis
In the following template for a gitlab-ci.yml-file only the main-Branch is cloned. It also works for any other Branch. This also works for any other branch. To clone a different branch, you need to change the TARGET_BRANCH variable.
Please note that you do not need to modify the variables CI_SERVER_FQDN and CI_PROJECT_PATH, as these are automatically set by GitLab in the CI/CD environment.
# CI to mirror our GitHub repository main branch to OpenCode GitLab main branch
stages:
- mirroring
variables:
GIT_DEPTH: 0
TARGET_BRANCH: main
TARGET_REPO: https://github.com/DeineGrupp/DeinProjekt.git
mirror_github_main:
stage: mirroring
image: alpine/git
before_script:
- apk update
- git config --global user.name "${GITLAB_USER_NAME}"
- git config --global user.email "${GITLAB_USER_EMAIL}"
# Clone $TARGET_BRANCH from GitHub
- git clone --branch ${TARGET_BRANCH} --single-branch ${TARGET_REPO} target_repo
- cd target_repo
# Add GitLab target remote with token
- git remote add target "https://${GITLAB_PAT_NAME}:${GITLAB_PAT}@${CI_SERVER_FQDN}/${CI_PROJECT_PATH}.git"
script:
- echo "Pushing GitHub main → GitLab main"
- git push target ${TARGET_BRANCH}:${TARGET_BRANCH}--force
- git push target --tags --force
rules:
- if: '${CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE} == "push" || ${CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE} == "schedule"'
2. Enable access to the source project¶
Note
Instead of enabling access via an access token, you can also set up access via an SSH key. To do this, you must also adjust the corresponding options in the .gitlab-ci.yml file.
On the GitLab page of the source project, navigate to Settings > Access Tokens. Create a new access token using the Add new token button:
- Assign a meaningful token name and make a note of this exact name (or save it in a password manager).
- Select the role
Developer. - Select the following scopes:
write_repository,read repository. - Confirm the creation of a new project access token by clicking the (blue) “Create project access token” button.
Then, on the page that has now opened, copy the newly created access token to the clipboard using the Copy project access token button (or save it in a password manager):
Add the created access token to the CI/CD variables:
- Now navigate to Settings > CI/CD in the navigation bar (on the left).
- Open the Variables tab.
- Click on the Add variable button.
- Now enter the value
GITLAB_PATin the Key field. - Add the access token from the clipboard (or password manager) from step 3 to the Value field (make sure that no new empty line is added at the end of the code).
- Now click on the Add Variable button.
Add the variable with the key GITLAB_PAT_NAME and the name of the access token from step 2 to the CI/CD variables.
Note
If mirroring does not work despite the variables being set correctly:
- Check branch protection: The branch used (e.g.,
pull-mirroring) must not be protected. Otherwise, no push from the pipeline is possible – even if Force push is enabled. If necessary, remove the branch protection under Repository > Protected Branches. - Check variable protection: The CI/CD variables
GITLAB_PATandGITLAB_PAT_NAMEmust not be marked as protected if they are used in an unprotected branch.
3. Set up regular synchronization¶
- On the GitLab project page, open Build > Pipeline Schedules.
- Click the (blue) Create a new pipeline schedule button.
- Enter a meaningful description for the pipeline schedule and select an interval pattern. Create the new pipeline schedule using the corresponding (blue) button.
4. Verify that CI/CD is successful¶
Open the Build > Pipeline tab in the target project. The results of the pipeline can be viewed there. Click on the pipeline to see if the synchronization was successful.